How Inclusive Design Reshaped Microsoft Products
Twenty years ago, I used to be a Windows operating system user and always asked myself; why is it so complicated? The screen is full of functions with minimum consideration for the user experience. In 2012, Microsoft released their Windows 8 with dramatic changes that can be easily spotted–I guess you noticed that too. Microsoft switches to a minimal user interface (UI), inclusive design, and more user-friendly features. So, what is the hidden secret behind this shift that affected the Windows operating system and all Microsoft products? It is the adoption of the design thinking process. Previously, we covered the application for the design thinking process in Apple, Google, and IBM. Today we will explore how Microsoft adopted design thinking in Microsoft’s product development process to achieve an inclusive design.
Microsoft is one of the leading giants in the technology market, supplying billions of users with operating systems, software and game applications. Their products were translated into 130 languages. In 2016, the company employed 114,000 employees with a net profit that reached USD$85.32 billion. The company has different design groups focusing on the user experience, including Microsoft’s User Experience Excellence group and Windows Live Web Communications user experience team.
Design in Microsoft
According to the Design Council publication Eleven Lessons: managing design in eleven global brands, Microsoft moved from a technology-centric to a user-centric company where inclusive design is essential in this new model. While technology (viability), business (feasibility), and design (usability) are essential for business success and achieving innovation, the third factor, the design, is essential to achieve universal design, solving the users’ problems and addressing their needs in the production process. Brad Weed, Director of User Experience at Microsoft, stated: “In 1993, design was a luxury. It is now generally accepted that design is critical to our success.”
Related articles:
- Practice Guide to Run a Google Design Sprint
- Design Thinking Case Study: Innovation at Apple
- IBM Design Thinking Model: A Shift Toward Big Enterprises
What is inclusive design?
Inclusive design is an approach that aims to consider all different users in the design process regardless of their background, demographic information, abilities, race, situation, ergonomics, financial status and more. This consideration reflects on the design outcome, technology, and business model. The notion of inclusive design can be extended to more than just people in the system thinking paradigm. It can include the different actors targeted with the outcome, such as how the design outcome may affect the environment around it (Check What is Inclusive Design? And How to Apply It?).

It is a good point to differentiate between universal design, accessible design and inclusive design. The universal design aims to provide a one-design solution that fits the diverse perspectives of users without considering the flexibility in the design to be suitable for each user’s needs. While the accessible design focuses only on the users with disabilities and how to design a user-friendly outcome for them, the inclusive design aims to produce an adaptive design that can be user-friendly for a wide range of users as possible. Developing an inclusive design is a challenging and long design process, as it involves user interaction to understand each user’s needs to consider in the inclusive product. This is why design thinking presents the key paradigm that companies such as Microsoft should manifest the principles of inclusive design in their design practice (The Double Diamond Design Thinking Process and How to Use it).
Inclusion Design in Microsoft
The inclusive design principles in Microsoft are based on three main parameters. The first is recognising exclusion, which is the first step in inclusion by identifying the knowledge bias and the users not considered in the existing products. After identifying this gap, the second principle is based on learning from diversity to get a true insight into their needs and experience, which is the key to identifying the changes needed in the current system and the inclusive design decision. Finally, the third principle is to extend the inclusion to as many users as possible (Download Microsoft Inclusive 101 Guidebook).
The inclusion design toolkit in Microsoft is based on understanding the cognitive exclusion in the process and overcoming it by understanding the reasons for failure, its significance, and how to frame this understanding to improve the system. Once this cognitive bias is understood, the teams can co-create with cognitive diversity in mind. This co-create practice is underpinned by applying design thinking principles (Download Microsoft Inclusive Design for Cognition Guidebook).
Adopting a Design Thinking Process to Achieve Inclusion
Design thinking is a discipline that addresses solving human problems through a set of tools, processes, and strategies that aim to put the consumer at the heart of the development process to create a product that can be considered technologically feasible and viable from the business perspective. In Microsoft’s Enterprise article, How design thinking can transform your business, Linda Shi highlights three main ways to adopt design thinking inside the organisation to foster innovation (Design Thinking Tools and Methods Complete Guide):
Achieve inclusion through empathy within the business strategy.
Empathy refers to clearly understanding people’s needs; this applies to both consumers and company employees. This understanding is then contributing to the holistic business strategy. To achieve inclusion design in the core of the design thinking process, the user problems need to be clearly defined in order to use it to ideate the solution in the form of a product or service, which is transformed in the Prototyping stage into a testable prototype.
Highlight the Importance of Prototyping.
At the core of the design thinking process, prototyping helps the stakeholders and users to visualise the solution to explore, test, and validate that it solves the user problem and reflects the business strategy.
Embrace the role of design inside the organisation
Design thinking helps to reshape the role of design and designers inside the organisation. The designers can contribute to the stakeholders to build a user-centric business strategy and ensure it is adopted through all the product development stages.
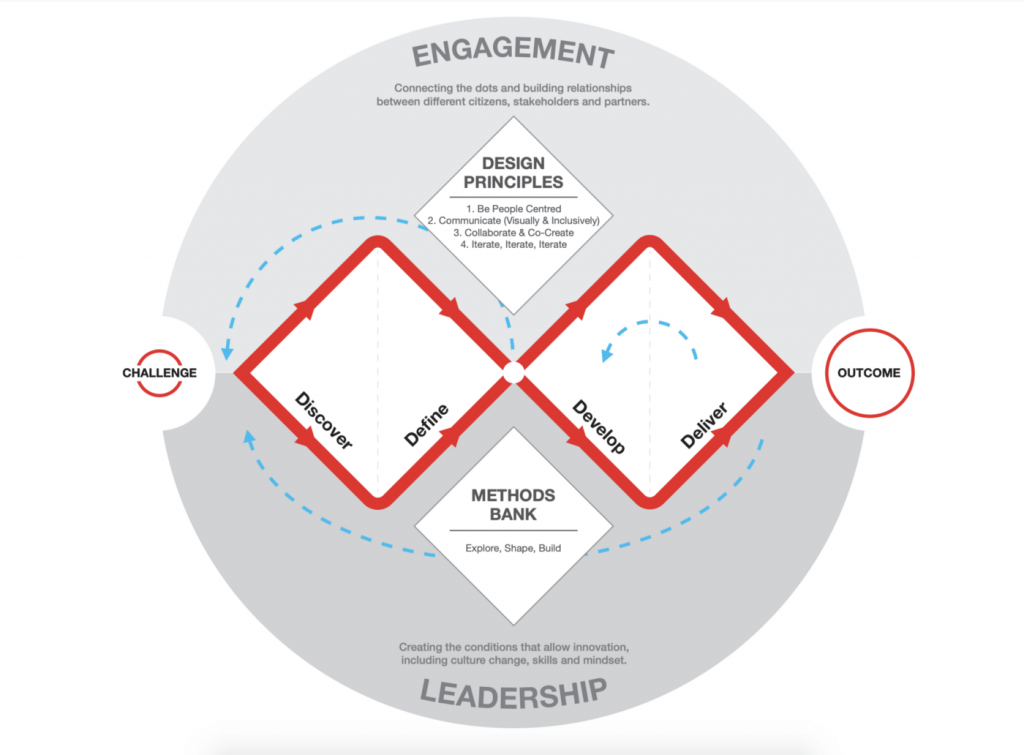
The Design Thinking in Microsoft
To achieve Microsoft’s target to build an inclusive product, the User Experience Excellence group managed by Surya V ank, a design process has been deployed, and it includes the following five cycles:
- Understand – this phase focuses on the ux research and gathering information about the user to observe and understand their needs.
- Envision – In this phase, the design team analyses the data collected from the understanding phase and uses it to think of the solution for the addressed problems.
- Specify – After sharing and discussing ideas, the design team define the solution and builds a detailed specification for the product.
- Implement – The product is developed based on the specifications highlighted in the previous cycle. This phase includes developing the prototypes and testing the product before releasing it to the market.
- Maintain – The product is a case of continuous evaluation and testing to apply these modifications in the next releases.
The Product Design Lead for the Windows Live Web Communication product team, Erez Kikin Gil, highlighted the implementation of another design process model consisting of four stages:
- Understand – This is the research stage that involves investigating the problem that needs to be addressed, ethnographic user research, and design research.
- Ideate – The team starts visualising the solution directly through sketches, user scenarios, and other prototyping tools. The stakeholders communicate in this phase to brainstorm and discuss new ideas to solve the user’s problems.
- Test – This stage runs through both the ideate and product cycle in order to test and evaluate the prototype and ensure it solves the user’s problems. Different tools are used in this phase, such as comparison studies, benchmarks, and product usability.
- Communicate – The previous stage’s results are shared with the stakeholders using different channels to ensure that the product is viable from different perspectives.
Product Example: Microsoft Surface Book
Surface Book is one of Microsoft’s newest products. A powerful laptop that merges between simple design, high performance, high battery life, and adaptability. Microsoft Surface Book can be used as a laptop to undergo heavy computer tasks or switched to a tablet device where users can easily use it with its drawing pen.
According to the review for the Surface Book insights by Danielle McClune, Microsoft Writer, we can highlight two main characteristics that contributed to building the new innovative product; Addressing user needs and prototyping. The focus on the user problems as the new product aimed to provide an easy-to-use laptop that users can hold with them anywhere and fold as a table device while maintaining its powerful specifications. It can run a regular laptop application, including heavy graphic applications and use the drawing pen to work with desktop applications.

The other characteristic is the intensive usage of prototyping to help the design team imagine, visualise, and test the different ideas. These prototypes played an essential role in reaching the product’s final shape. Kait Schoeck, Industrial Designer, highlighted: “We always joke that we could fill this whole building with prototypes,” he continued “, It is for real. We made more models on this project than ever before.”
The prototypes created for the Surface Book also help the team communicate with other industrial designers in the company to test and give feedback on the product to validate how it solves the user problem through an innovative approach. Hua Wang, Industrial Designer, comments on the Surface Book: “It’s quite incredible what we did here because you can detach it, but when it’s attached, it looks like one piece.”
Reduce the Cognitive Load: Microsoft Developer Tools – Visual Studio Intellicode
In this case study, the Microsoft team aimed to address two challenges. The first is to balance between discoverability and interruption for development while working with code. The second is to present the code to developers most effectively. In this regard, the team implemented inclusive design to work with a wide range of existing users, including users who have ADHD and find problems in focus. Two main findings were identified: the code suggestions appress automatically and fast, and the hints bar is hard to find.
The team implemented co-design to work with users to solve the problem and reduce the cognitive heavy experience for users. The final solution involved improving the inline cover serration suggestions and enhancing the inline-single-line code change suggestions.
Conclusion
Inclusive design is essential to address a broader range of users’ needs and reduce the team’s biases resulting from excluding users who may vary in their needs. Microsoft shifted toward inclusive design and co-design to target users’ challenges and improve their experience. The strategy involved implementing design methodologies such as design thinking. The first mini case study provided a successful example of how design thinking can contribute to reshaping a giant company such as Microsoft toward focusing on the user’s needs through building a user-centric strategy. While two design processes are applied in two different products, both models share the exact characteristics of the design thinking process. Another lesson from this case study is that companies may create or alter the design stages to fit with their product development process as long as they follow the characteristics of the design thinking that move through research, ideation, prototype, and testing. We have seen this adaption of the design process in previous examples in IBM, Google, and Apple.
The Microsoft Surface Book provided a successful example of how focusing on user needs and prototyping can contribute to building an innovative product. The Surface Book is an excellent example of the outcome of adopting the design process and the new product development process. Although the large structure of the organisation, Microsoft provided a successful example that other companies on different scales can follow.
In the second mini case study, we saw how Microsoft used co-design to improve their Visual Studio Intellicode to address a broader range of users, including users with ADHD, who needed to have more focus and a less distracting experience.
The implementation of inclusive design in Microsoft provides an example for companies to shift their strategy toward a design-centred strategy which can help them focus on their users’ needs and improve their experience.
Note: This article was first published in 13rd May 2017